
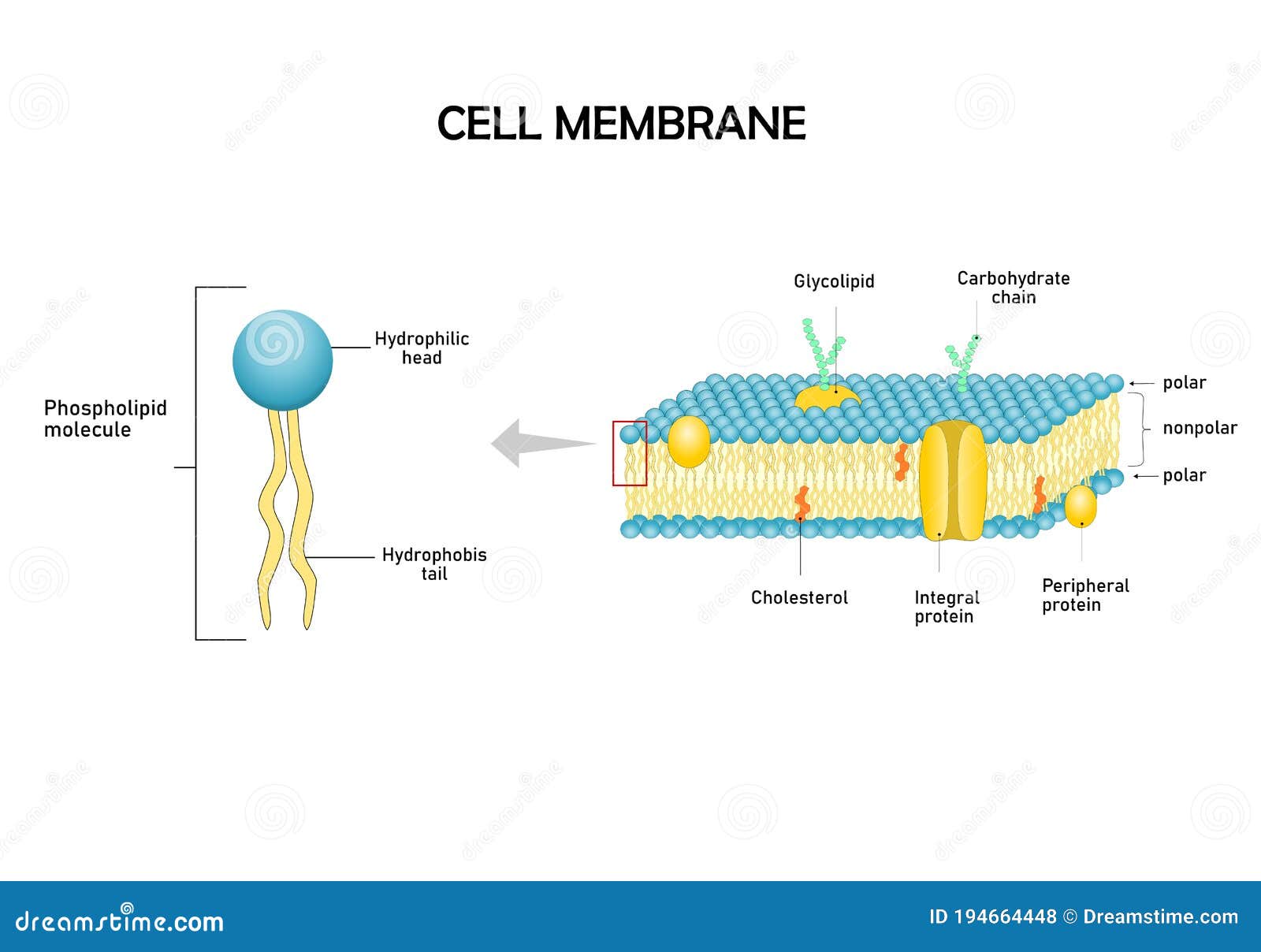
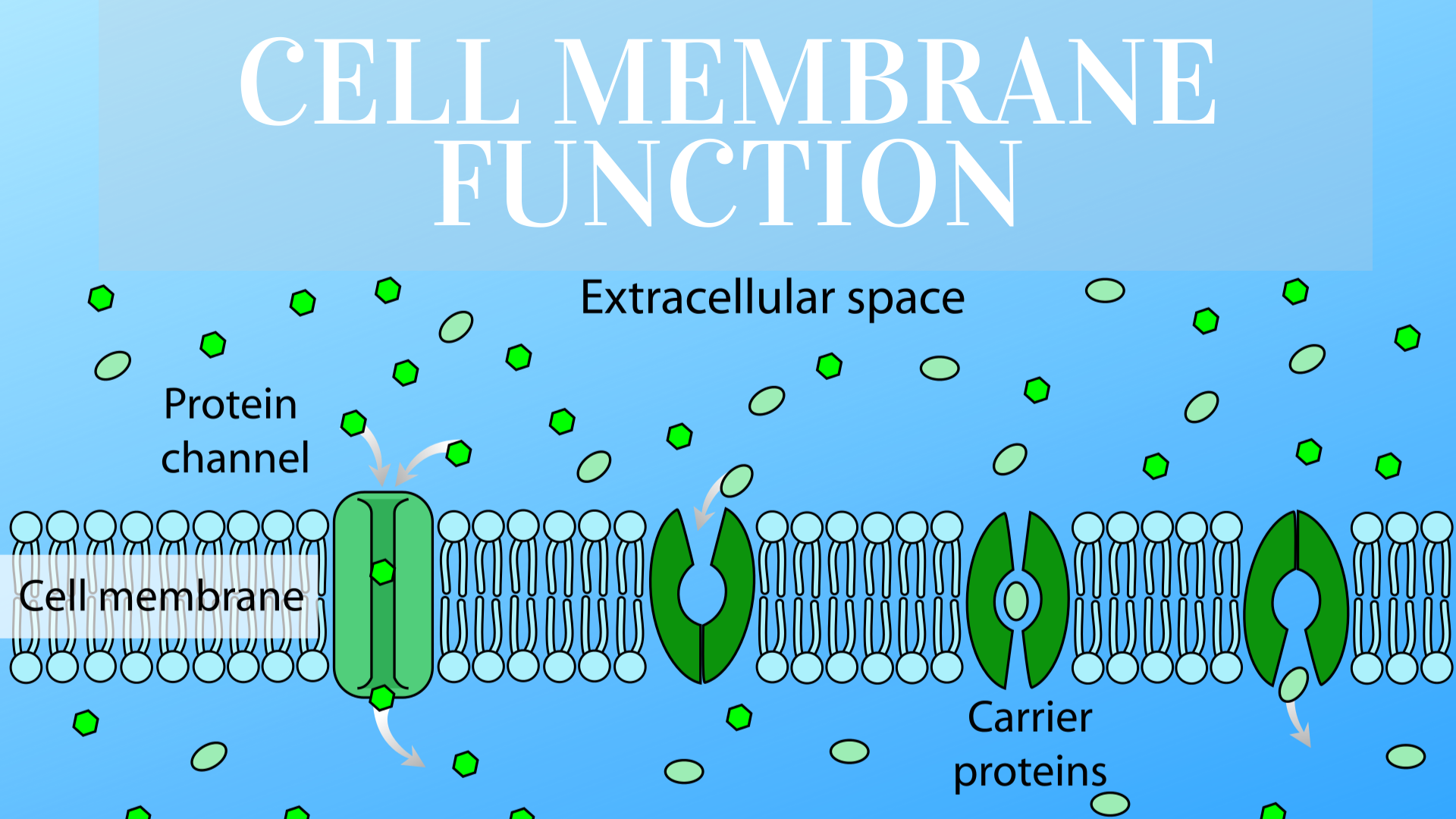
In any solution, solute particles move constantly.Cellular cytoplasm consists of many different substances dissolved in water.Equilibrium= when the amount of substances (concentration) is the SAME in both places.Concentration Gradient= when the amount of substances (concentration) is different in two places.Meaning, that some substances can pass across them and others cannot.Most biological membranes are selectively permeable.Although many substances can cross biological membranes, some are too large or too strongly charged to cross the lipid bilayer.Act like chemical identification cards, allowing individual cells to identify one another.Form channels or pumps that help move materials across the cell membrane.Because the proteins embedded in the lipid bilayer can mover around and “float” among the lipids, and because so many different kinds of molecules make up the cell membrane, scientists call the cell membrane a “fluid mosaic”.Embedded in the lipid bilayer of most cell membranes are protein molecules, carbohydrates molecules are attached to many of these proteins.When these lipids are mixed with water, their hydrophobic fatty acid “tails” cluster together while their hydrophilic “heads” are attracted to water.The fatty acid portion of a phospholipid is hydrophobic (“water-fearing”), while the opposite end of the molecule (the head) is hydrophilic (“water-loving”).The layered structure of cell membranes reflects the chemical properties of the lipids that make them up.The lipid bilayer gives cell membranes a flexible structure that forms a strong barrier between the cell and its surroundings.All cells contain cell membranes, which almost always are made up of a double-layered sheet called a lipid bilayer.Least common of the membrane lipids (ca.Amphipathic: hydrophobic and hydrophilic.Major lipid component of most biomembranes.Glycolipids and glycoproteins (lipids and proteins with attached carbohydrates).
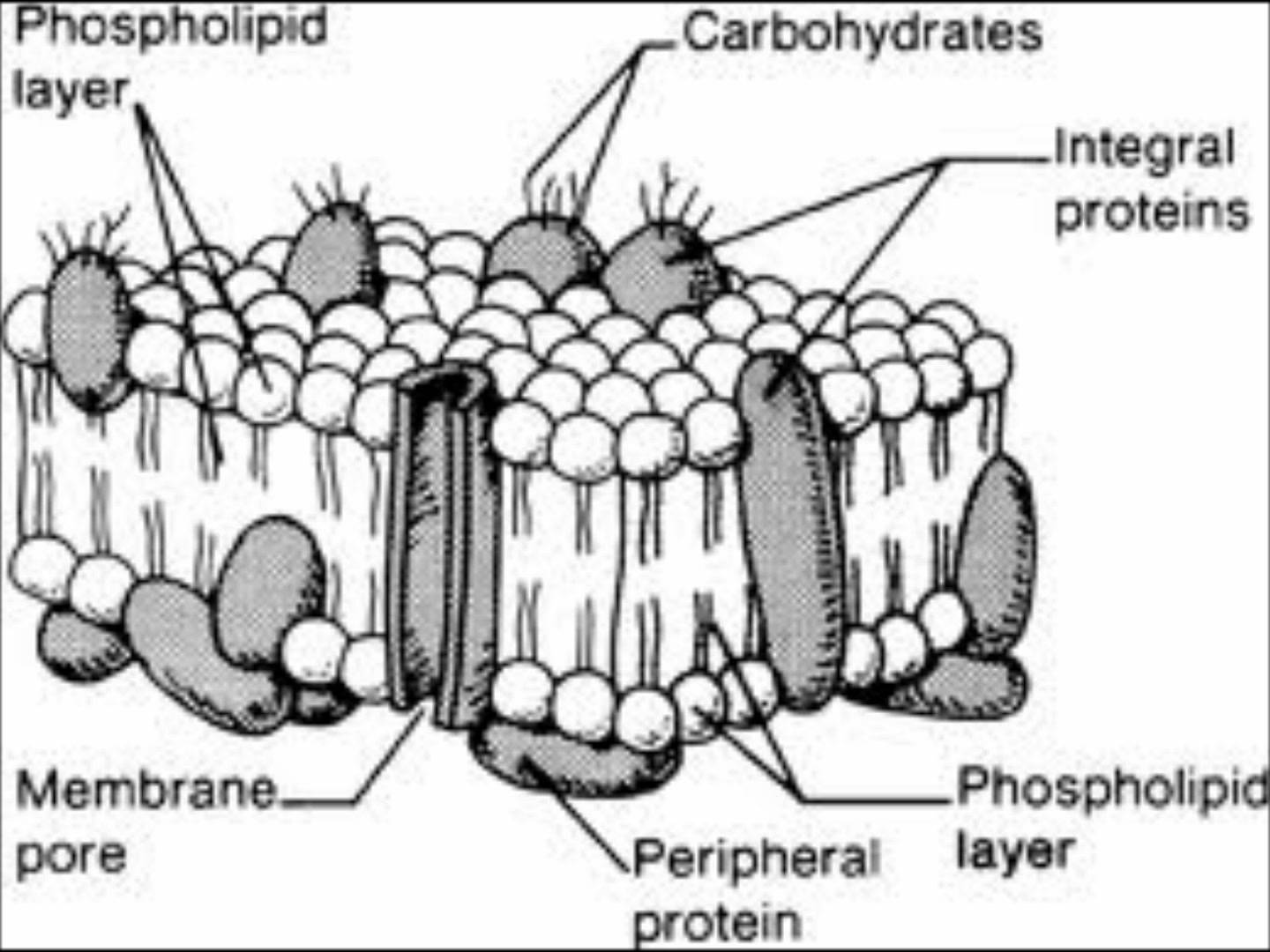
Internal membranes define a variety of cell organelles.Cell (plasma) membrane: defines cell boundaries.Describe various membrane transport pumps including their energy source, stoichiometry and functional significance.Describe the processes by which small solutes, ions and macromolecules cross biomembranes.Describe the structural relationship among the components of the membrane and general functional roles served by each of them.Brown, PhD BC21D: Bioenergetics & Metabolism Biomembrane Structure and Function Paul D.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
